what kind of attack simulation detects vulnerabilities and attempts to exploit them
Acyber attack is any type of offensive activeness that targets computer information systems, infrastructures, computer networks or personal figurer devices, using various methods to steal, alter or destroy information or information systems.
Today I'll depict the 10 most mutual cyber attack types:
- Denial-of-service (DoS) and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attack
- Phishing and spear phishing attacks
- Drive-by attack
- Countersign attack
- SQL injection attack
- Cross-site scripting (XSS) set on
- Eavesdropping attack
- Birthday assail
- Malware assail
1. Denial-of-service (DoS) and distributed deprival-of-service (DDoS) attacks
A denial-of-service set on overwhelms a system's resources and so that it cannot answer to service requests. A DDoS attack is also an attack on system's resources, but it is launched from a large number of other host machines that are infected by malicious software controlled by the attacker.
Unlike attacks that are designed to enable the attacker to proceeds or increment access, denial-of-service doesn't provide direct benefits for attackers. For some of them, it'south enough to have the satisfaction of service denial. Still, if the attacked resources belongs to a business competitor, and then the benefit to the attacker may be existent plenty. Some other purpose of a DoS set on can be to accept a system offline then that a different kind of attack can be launched. 1 common example is session hijacking, which I'll draw after.
There are dissimilar types of DoS and DDoS attacks; the near common are TCP SYN flood attack, teardrop assault, smurf attack, ping-of-death attack and botnets.
TCP SYN flood attack
In this assail, an assailant exploits the utilise of the buffer space during a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) session initialization handshake. The attacker'south device floods the target system'southward small in-process queue with connection requests, merely it does not respond when the target system replies to those requests. This causes the target organisation to time out while waiting for the response from the attacker's device, which makes the system crash or become unusable when the connection queue fills upwardly.
There are a few countermeasures to a TCP SYN alluvion attack:
- Place servers behind a firewall configured to stop entering SYN packets.
- Increase the size of the connectedness queue and decrease the timeout on open connections.
Teardrop set on
This attack causes the length and fragmentation offset fields in sequential Internet Protocol (IP) packets to overlap one another on the attacked host; the attacked system attempts to reconstruct packets during the process just fails. The target arrangement then becomes confused and crashes.
If users don't have patches to protect against this DoS attack, disable SMBv2 and block ports 139 and 445.
Smurf attack
This attack involves using IP spoofing and the ICMP to saturate a target network with traffic. This attack method uses ICMP repeat requests targeted at broadcast IP addresses. These ICMP requests originate from a spoofed "victim" address. For instance, if the intended victim address is 10.0.0.10, the attacker would spoof an ICMP echo request from x.0.0.x to the broadcast address 10.255.255.255. This request would go to all IPs in the range, with all the responses going back to 10.0.0.10, overwhelming the network. This procedure is repeatable, and can be automated to generate huge amounts of network congestion.
To protect your devices from this assault, you need to disable IP-directed broadcasts at the routers. This will prevent the ICMP echo broadcast request at the network devices. Another option would exist to configure the end systems to keep them from responding to ICMP packets from broadcast addresses.
Ping of expiry assail
This type of attack uses IP packets to 'ping a target arrangement with an IP size over the maximum of 65,535 bytes. IP packets of this size are not allowed, so aggressor fragments the IP package. Once the target system reassembles the packet, it can experience buffer overflows and other crashes.
Ping of death attacks can be blocked by using a firewall that will check fragmented IP packets for maximum size.
Botnets
Botnets are the millions of systems infected with malware nether hacker control in order to carry out DDoS attacks. These bots or zombie systems are used to bear out attacks against the target systems, frequently overwhelming the target system's bandwidth and processing capabilities. These DDoS attacks are hard to trace because botnets are located in differing geographic locations.
Botnets tin exist mitigated past:
- RFC3704 filtering, which will deny traffic from spoofed addresses and assistance ensure that traffic is traceable to its correct source network. For example, RFC3704 filtering will drib packets from bogon list addresses.
- Blackness hole filtering, which drops undesirable traffic earlier it enters a protected network. When a DDoS assail is detected, the BGP (Edge Gateway Protocol) host should send routing updates to ISP routers and so that they route all traffic heading to victim servers to a null0 interface at the next hop.
2. Man-in-the-heart (MitM) attack
A MitM attack occurs when a hacker inserts itself between the communications of a client and a server. Here are some common types of human-in-the-middle attacks:
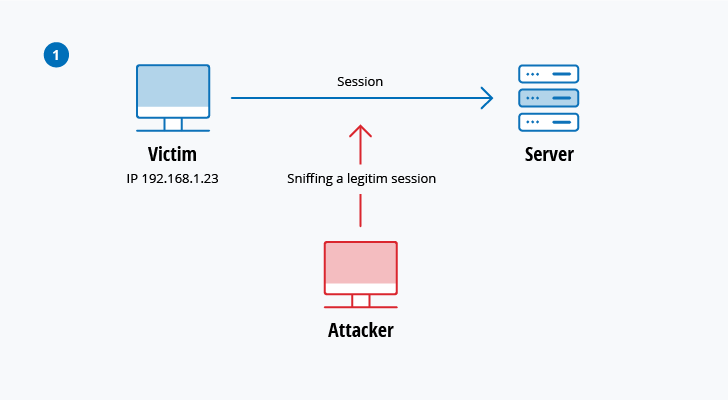
Session hijacking
In this type of MitM attack, an aggressor hijacks a session between a trusted client and network server. The attacking reckoner substitutes its IP accost for the trusted client while the server continues the session, assertive it is communicating with the customer. For case, the attack might unfold like this:
- A customer connects to a server.
- The attacker's estimator gains command of the client.
- The attacker's computer disconnects the customer from the server.
- The attacker'south estimator replaces the client's IP address with its own IP address and
spoofs the client's sequence numbers. - The aggressor's computer continues dialog with the server and the server believes it is still communicating with the customer.
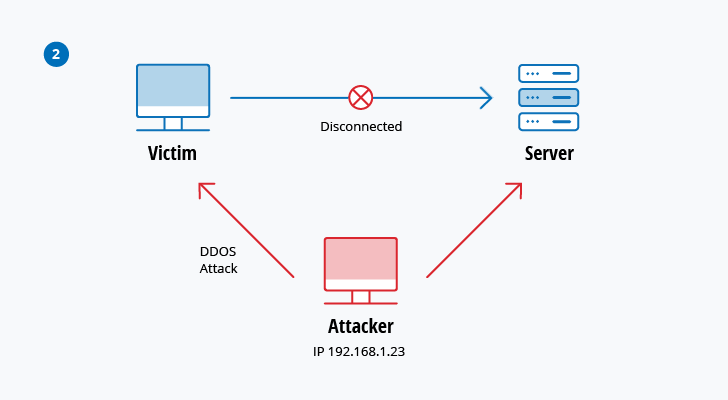
IP Spoofing
IP spoofing is used by an assailant to convince a system that it is communicating with a known, trusted entity and provide the attacker with admission to the system. The assaulter sends a bundle with the IP source address of a known, trusted host instead of its ain IP source accost to a target host. The target host might accept the bundle and deed upon it.
Replay
A replay attack occurs when an attacker intercepts and saves old letters then tries to send them later, impersonating one of the participants. This type can be easily countered with session timestamps or nonce (a random number or a string that changes with time).
Currently, there is no single technology or configuration to prevent all MitM attacks. Generally, encryption and digital certificates provide an effective safeguard confronting MitM attacks, assuring both the confidentiality and integrity of communications. But a human-in-the-center set on can be injected into the middle of communications in such a mode that encryption will non aid — for example, attacker "A" intercepts public key of person "P" and substitute it with his own public key. Then, anyone wanting to send an encrypted message to P using P's public key is unknowingly using A's public fundamental. Therefore, A can read the message intended for P and and then send the message to P, encrypted in P's real public fundamental, and P will never detect that the bulletin was compromised. In addition, A could also modify the message before resending information technology to P. As you can come across, P is using encryption and thinks that his information is protected but it is not, because of the MitM attack.
So, how tin can you make sure that P's public key belongs to P and non to A? Certificate authorities and hash functions were created to solve this problem. When person 2 (P2) wants to transport a bulletin to P, and P wants to be certain that A volition non read or modify the message and that the bulletin actually came from P2, the following method must be used:
- P2 creates a symmetric cardinal and encrypts information technology with P's public primal.
- P2 sends the encrypted symmetric central to P.
- P2 computes a hash part of the message and digitally signs it.
- P2 encrypts his bulletin and the bulletin's signed hash using the symmetric key and sends the entire matter to P.
- P is able to receive the symmetric key from P2 because only he has the private key to decrypt the encryption.
- P, and only P, can decrypt the symmetrically encrypted message and signed hash because he has the symmetric central.
- He is able to verify that the message has not been altered considering he can compute the hash of received bulletin and compare it with digitally signed ane.
- P is besides able to bear witness to himself that P2 was the sender because but P2 can sign the hash and so that information technology is verified with P2 public key.
3. Phishing and spear phishing attacks
Phishing set on is the practise of sending emails that appear to exist from trusted sources with the goal of gaining personal information or influencing users to practise something. Information technology combines social engineering and technical trickery. Information technology could involve an zipper to an email that loads malware onto your figurer. It could besides exist a link to an illegitimate website that tin trick you into downloading malware or handing over your personal information.
Spear phishing is a very targeted type of phishing activity. Attackers take the time to conduct inquiry into targets and create messages that are personal and relevant. Because of this, spear phishing can be very hard to place and fifty-fifty harder to defend against. One of the simplest ways that a hacker can conduct a spear phishing attack is electronic mail spoofing, which is when the information in the "From" section of the email is falsified, making it appear as if it is coming from someone you know, such as your management or your partner company. Another technique that scammers use to add credibility to their story is website cloning — they copy legitimate websites to fool you into entering personally identifiable information (PII) or login credentials.
To reduce the risk of being phished, yous tin utilise these techniques:
- Critical thinking — Exercise not have that an electronic mail is the real deal just because y'all're busy or stressed or you accept 150 other unread messages in your inbox. Stop for a minute and analyze the electronic mail.
- Hovering over the links — Move your mouse over the link, only practise not click information technology! Just let your mouse cursor h over over the link and see where would actually take yous. Apply critical thinking to decipher the URL.
- Analyzing email headers — Email headers ascertain how an email got to your address. The "Answer-to" and "Return-Path" parameters should lead to the aforementioned domain equally is stated in the e-mail.
- Sandboxing — Yous tin can test electronic mail content in a sandbox environment, logging activity from opening the attachment or clicking the links inside the email.
4. Bulldoze-past assail
Drive-by download attacks are a common method of spreading malware. Hackers await for insecure websites and plant a malicious script into HTTP or PHP lawmaking on 1 of the pages. This script might install malware directly onto the calculator of someone who visits the site, or it might re-direct the victim to a site controlled by the hackers. Drive-by downloads tin happen when visiting a website or viewing an email message or a popular-up window. Different many other types of cyber security attacks, a drive-by doesn't rely on a user to do anything to actively enable the attack — y'all don't take to click a download button or open a malicious email attachment to become infected. A drive-by download can have reward of an app, operating system or web browser that contains security flaws due to unsuccessful updates or lack of updates.
To protect yourself from drive-by attacks, you lot need to keep your browsers and operating systems up to date and avoid websites that might incorporate malicious code. Stick to the sites you normally apply — although go on in mind that even these sites can be hacked. Don't continue too many unnecessary programs and apps on your device. The more plug-ins you lot accept, the more vulnerabilities in that location are that can exist exploited by drive-past attacks.
five. Password assault
Because passwords are the most unremarkably used mechanism to authenticate users to an data system, obtaining passwords is a common and effective attack arroyo. Access to a person's password tin can be obtained by looking around the person's desk, ''sniffing'' the connection to the network to learn unencrypted passwords, using social engineering, gaining admission to a countersign database or outright guessing. The last approach can be washed in either a random or systematic manner:
- Beast-force password guessing means using a random approach by trying different passwords and hoping that i piece of work Some logic can be applied by trying passwords related to the person'southward proper noun, job title, hobbies or similar items.
- In a lexicon attack, a dictionary of common passwords is used to effort to gain access to a user'south reckoner and network. One approach is to copy an encrypted file that contains the passwords, utilize the same encryption to a dictionary of commonly used passwords, and compare the results.
In order to protect yourself from dictionary or brute-force attacks, you lot need to implement an account lockout policy that will lock the business relationship afterward a few invalid password attempts. Yous tin can follow these account lockout all-time practices in social club to set up it upwardly correctly.
6. SQL injection attack
SQL injection has become a common consequence with database-driven websites. It occurs when a malefactor executes a SQL query to the database via the input data from the client to server. SQL commands are inserted into data-aeroplane input (for example, instead of the login or countersign) in order to run predefined SQL commands. A successful SQL injection exploit tin read sensitive information from the database, modify (insert, update or delete) database information, execute assistants operations (such equally shutdown) on the database, recover the content of a given file, and, in some cases, issue commands to the operating system.
For example, a web form on a website might request a user's account name so send it to the database in guild to pull up the associated account information using dynamic SQL like this:
"SELECT * FROM users WHERE account = '" + userProvidedAccountNumber +"';"
While this works for users who are properly entering their business relationship number, information technology leaves a hole for attackers. For case, if someone decided to provide an account number of "' or '1' = 'one'", that would result in a query string of:
"SELECT * FROM users WHERE account = '' or '1' = 'i';"
Because '1' = 'i' always evaluates to Truthful, the database will return the data for all users instead of just a unmarried user.
The vulnerability to this type of cyber security attack depends on the fact that SQL makes no real distinction between the control and data planes. Therefore, SQL injections piece of work mostly if a website uses dynamic SQL. Additionally, SQL injection is very common with PHP and ASP applications due to the prevalence of older functional interfaces. J2EE and ASP.NET applications are less likely to have easily exploited SQL injections because of the nature of the programmatic interfaces available.
In guild to protect yourself from a SQL injection attacks, apply least0privilege model of permissions in your databases. Stick to stored procedures (brand certain that these procedures don't include whatsoever dynamic SQL) and prepared statements (parameterized queries). The code that is executed against the database must be strong plenty to prevent injection attacks. In add-on, validate input information confronting a white list at the application level.
7. Cross-site scripting (XSS) set on
XSS attacks use third-party web resources to run scripts in the victim's web browser or scriptable application. Specifically, the attacker injects a payload with malicious JavaScript into a website's database. When the victim requests a page from the website, the website transmits the page, with the attacker'southward payload every bit part of the HTML body, to the victim's browser, which executes the malicious script. For example, it might send the victim'south cookie to the attacker'southward server, and the attacker tin can extract it and utilize it for session hijacking. The virtually dangerous consequences occur when XSS is used to exploit additional vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities can enable an attacker to not only steal cookies, but likewise log cardinal strokes, capture screenshots, discover and collect network information, and remotely access and control the victim'due south automobile.
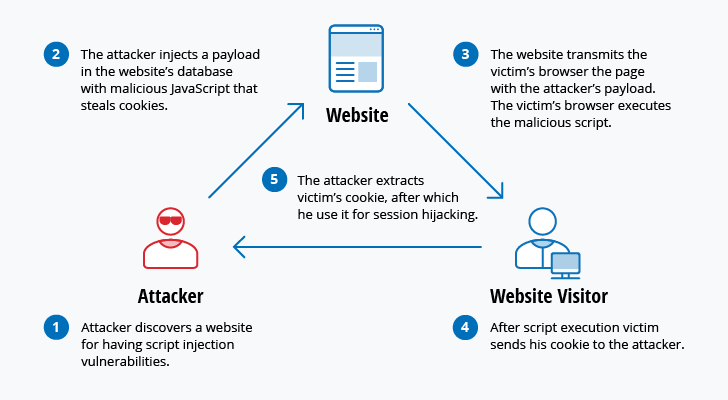
While XSS tin be taken advantage of inside VBScript, ActiveX and Wink, the virtually widely abused is JavaScript — primarily because JavaScript is supported widely on the spider web.
To defend against XSS attacks, developers can sanitize data input by users in an HTTP request before reflecting it back. Make sure all data is validated, filtered or escaped earlier echoing anything back to the user, such as the values of query parameters during searches. Convert special characters such every bit ?, &, /, <, > and spaces to their respective HTML or URL encoded equivalents. Give users the option to disable client-side scripts.
viii. Eavesdropping attack
Eavesdropping attacks occur through the interception of network traffic. By eavesdropping, an assailant can obtain passwords, credit menu numbers and other confidential data that a user might be sending over the network. Eavesdropping can be passive or agile:
- Passive eavesdropping — A hacker detects the information by listening to the message transmission in the network.
- Active eavesdropping — A hacker actively grabs the information by disguising himself as friendly unit of measurement and past sending queries to transmitters. This is chosen probing, scanning or tampering.
Detecting passive eavesdropping attacks is frequently more than important than spotting active ones, since active attacks requires the aggressor to gain noesis of the friendly units by conducting passive eavesdropping before.
Data encryption is the best countermeasure for eavesdropping.
9. Birthday attack
Birthday attacks are made confronting hash algorithms that are used to verify the integrity of a message, software or digital signature. A message processed past a hash part produces a message digest (MD) of fixed length, independent of the length of the input message; this Md uniquely characterizes the message. The altogether assail refers to the probability of finding two random letters that generate the same MD when processed by a hash role. If an assailant calculates same Medico for his message as the user has, he tin safely replace the user's bulletin with his, and the receiver will not be able to detect the replacement even if he compares MDs.
ten. Malware set on
Malicious software tin can be described as unwanted software that is installed in your system without your consent. It tin adhere itself to legitimate lawmaking and propagate; it tin can lurk in useful applications or replicate itself beyond the Cyberspace. Here are some of the almost common types of malware:
- Macro viruses — These viruses infect applications such as Microsoft Word or Excel. Macro viruses attach to an application's initialization sequence. When the application is opened, the virus executes instructions before transferring command to the application. The virus replicates itself and attaches to other lawmaking in the computer system.
- File infectors — File infector viruses usually attach themselves to executable code, such as .exe files. The virus is installed when the code is loaded. Another version of a file infector associates itself with a file past creating a virus file with the aforementioned proper noun, but an .exe extension. Therefore, when the file is opened, the virus code will execute.
- System or boot-tape infectors — A kicking-record virus attaches to the master kicking record on difficult disks. When the system is started, information technology will look at the kicking sector and load the virus into retentiveness, where information technology can propagate to other disks and computers.
- Polymorphic viruses — These viruses conceal themselves through varying cycles of encryption and decryption. The encrypted virus and an associated mutation engine are initially decrypted by a decryption program. The virus proceeds to infect an area of code. The mutation engine then develops a new decryption routine and the virus encrypts the mutation engine and a re-create of the virus with an algorithm corresponding to the new decryption routine. The encrypted parcel of mutation engine and virus is attached to new lawmaking, and the procedure repeats. Such viruses are difficult to detect simply have a high level of entropy because of the many modifications of their source lawmaking. Anti-virus software or complimentary tools like Process Hacker can utilise this feature to notice them.
- Stealth viruses — Stealth viruses take over organisation functions to conceal themselves. They practise this past compromising malware detection software so that the software will report an infected surface area as beingness uninfected. These viruses conceal any increase in the size of an infected file or changes to the file'due south date and time of terminal modification.
- Trojans — A Trojan or a Trojan horse is a program that hides in a useful programme and normally has a malicious function. A major difference between viruses and Trojans is that Trojans do not self-replicate. In add-on to launching attacks on a system, a Trojan tin establish a dorsum door that tin be exploited by attackers. For example, a Trojan can be programmed to open a high-numbered port so the hacker can use information technology to listen and so perform an assail.
- Logic bombs — A logic bomb is a blazon of malicious software that is appended to an application and is triggered by a specific occurrence, such as a logical condition or a specific date and time.
- Worms — Worms differ from viruses in that they do non attach to a host file, merely are self-contained programs that propagate across networks and computers. Worms are commonly spread through email attachments; opening the attachment activates the worm program. A typical worm exploit involves the worm sending a copy of itself to every contact in an infected computer's email address In improver to conducting malicious activities, a worm spreading across the internet and overloading email servers can result in denial-of-service attacks against nodes on the network.
- Droppers — A dropper is a program used to install viruses on computers. In many instances, the dropper is not infected with malicious lawmaking and, therefore might not exist detected by virus-scanning software. A dropper can also connect to the internet and download updates to virus software that is resident on a compromised organisation.
- Ransomware — Ransomware is a type of malware that blocks access to the victim's data and threatens to publish or delete information technology unless a ransom is paid. While some unproblematic computer ransomware tin lock the system in a manner that is non difficult for a knowledgeable person to contrary, more avant-garde malware uses a technique called cryptoviral extortion, which encrypts the victim'southward files in a style that makes them about impossible to recover without the decryption cardinal.
- Adware — Adware is a software application used by companies for marketing purposes; advertisement banners are displayed while whatever program is running. Adware tin can exist automatically downloaded to your system while browsing any website and can exist viewed through popular-upwardly windows or through a bar that appears on the computer screen automatically.
- Spyware — Spyware is a blazon of programme that is installed to collect information about users, their computers or their browsing habits. Information technology tracks everything you practice without your knowledge and sends the data to a remote user. It besides can download and install other malicious programs from the cyberspace. Spyware works like adware merely is unremarkably a split up program that is installed unknowingly when you lot install another freeware application.
Decision
Mounting a good defense force requires understanding the offense. This commodity has reviewed the x most common cyber-security attacks that hackers utilize to disrupt and compromise information systems. Every bit y'all can encounter, attackers accept many options, such equally DDoS assaults, malware infection, human being-in-the-center interception, and creature-strength password guessing, to trying to proceeds unauthorized access to critical infrastructures and sensitive information.
Measures to mitigate these threats vary, merely security nuts stay the same: Go on your systems and anti-virus databases upwards to date, train your employees, configure your firewall to whitelist only the specific ports and hosts you need, keep your passwords stiff, use a least-privilege model in your IT environment, make regular backups, and continuously audit your IT systems for suspicious activeness.

Source: https://blog.netwrix.com/2018/05/15/top-10-most-common-types-of-cyber-attacks/
0 Response to "what kind of attack simulation detects vulnerabilities and attempts to exploit them"
Post a Comment